Let’s clear up the biggest myth in singing: that a great voice is something you’re either born with or not. The truth is, your voice is an instrument. Like any instrument, it gets better with smart, consistent practice.
Many singers who practice at home, however, hit the same frustrating walls running out of breath, cracking on high notes, or just not feeling confident in their pitch.
This guide is built to break down those walls. We’ll focus on the foundational techniques of breath, pitch, and consistency that create real, audible improvement, no professional studio required.
This guide covers these core skills and does not get into advanced performance or complex music theory.
Key Takeaways
- Master Your Breath: Proper diaphragmatic breathing is the non-negotiable foundation of a strong, stable voice.
- Warm-Up Every Time: A consistent 5-minute warm-up prevents vocal strain and prepares your voice for effective practice.
- Fix Pitch Problems: Use ear training and targeted exercises to move from guessing notes to hitting them accurately.
- Practice Consistently: Short, focused daily sessions (20-30 minutes) yield far better results than long, infrequent ones.
First, Master Your Engine: Breath Control & Posture
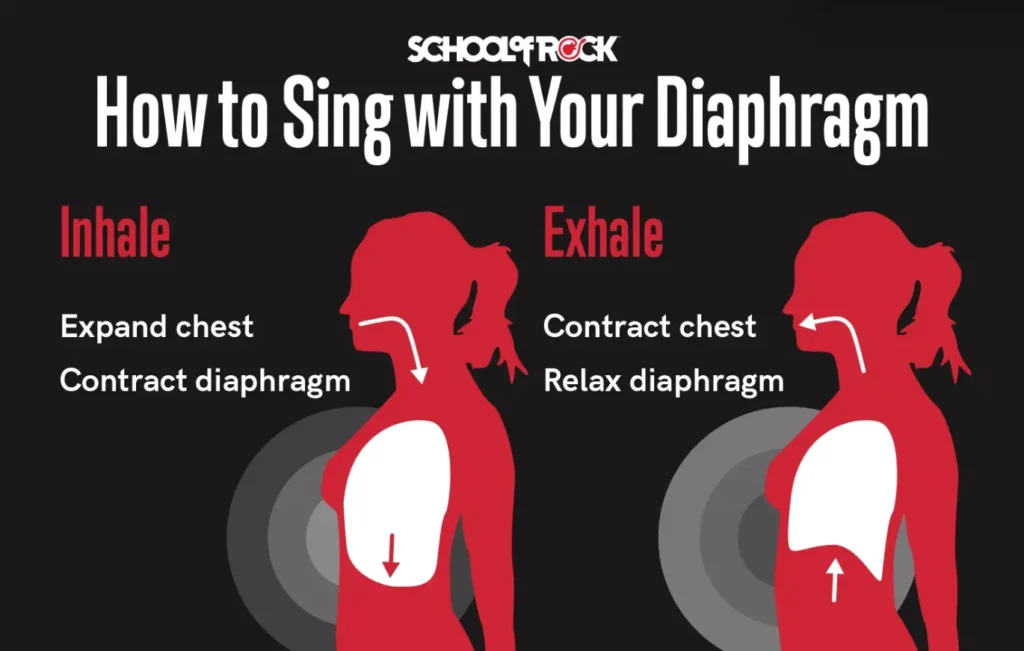
A supported voice starts with deep, controlled, and silent breathing. Before singing a single note, the first win is mastering diaphragmatic breathing, which is the powerhouse behind every great singer. Instead of taking shallow sips of air into your chest, focus on breathing low into your belly.
Place a hand on your stomach; it should expand outward as you inhale and gently contract as you exhale. This technique provides the steady stream of air needed to support long phrases and protect your vocal folds from strain.
Good posture shoulders back, chest open, and spine aligned is the framework that allows this engine to run efficiently.
Your 5-Minute Daily Vocal Warm-Up Routine
Singing on a “cold” voice is one of the fastest ways to cause vocal strain. Just like an athlete stretches before a game, a singer must prepare their vocal cords with a simple warm-up. This quick routine will get your voice ready for a productive practice session.
Exercise 1: The Lip Trill (The “Motorboat”)
Start by blowing air through your closed, relaxed lips to create a “motorboat” or “raspberry” sound. Glide this trill up and down your vocal range gently.
The lip trill is fantastic because it promotes steady airflow from your diaphragm and releases unnecessary tension in your lips and throat, all without putting any stress on your vocal cords. Do this for about 90 seconds.
Exercise 2: The Pitch Siren on an “Ooh” Vowel
On a soft “ooh” vowel (as in “who”), slide your voice from your lowest comfortable note to your highest, like a gentle siren. The key is to keep the sound smooth and connected, avoiding any breaks or cracks.
This exercise helps bridge the gap between your lower register (chest voice) and your upper register (head voice), promoting a unified, flexible vocal range. Repeat this for two to three minutes.
The #1 Mistake Most Self-Taught Singers Make (And How to Fix It)
The most common habit that holds singers back is forcing sound from the throat. This often happens in an effort to sound louder or hit higher notes, creating tension in the throat, jaw, and neck. The result is a strained, thin tone that can lead to vocal fatigue or even damage.
The Fix: Go back to the foundation breath support. Practice sustaining a single note on a vowel, like “ah.” Your goal is to keep the note perfectly steady, without wavering, purely by controlling the exhale from your diaphragm.
Your throat should feel relaxed and open, as if you’re yawning. This shifts the workload from the small, delicate muscles in your throat to the large, powerful muscles in your core.
How to Find Your Pitch and Actually Sing in Tune
Improving pitch accuracy is a trainable skill that combines ear training with vocal control. It comes down to training your ear to hear a note correctly and then training your voice to produce it.
Start by playing a note on a piano or a digital tuner app on your phone. Hum the note first, then sing it on a vowel. Record yourself and listen back. Are you sharp (too high) or flat (too low)?
This is where a good pair of headphones makes a huge difference. Knowing how to choose headphones helps you catch every little detail in your playback.
Case Study: From Vocal Strain to Strength
Consider a common scenario: a singer who can barely get through a chorus without their voice cracking on the high notes. Often, this singer has passion but relies entirely on throat muscle, believing they just don’t have the “range.” An effective solution is to strip practice back to zero.
For the first week, the focus shouldn’t be on singing songs at all, but on silent, diaphragmatic breathing exercises and gentle lip trills. By re-establishing this foundation and then adding sustained notes with a focus on core support, the change can be dramatic.
This shift in mechanics is how a singer goes from cracking on high notes to holding them for seconds longer.
Essential Gear for Practicing Smarter, Not Harder
While you don’t need a professional studio, a few key tools can dramatically accelerate your progress. First, a reliable digital tuner app is non-negotiable for pitch practice. Second, using even a basic microphone to record yourself is one of the most powerful tools for self-assessment.
Understanding the different types of microphones can help you pick the right one for your goals. Listening back to a recording gives you an objective perspective that is a cornerstone of any basic home recording studio.
Many resources now make it easier to learn to sing better at home by providing guidance on exercises, breathing control, and posture that support long-term improvement.
Conclusion
Remember that myth about singers being born, not made? By now, you should see that’s not true. Improving your voice at home is a journey of small, consistent steps.
By focusing on the fundamentals of breath, warming up properly, and training your ear, you’re building a reliable, strong, and healthy voice. Embrace the process, be patient with yourself, and celebrate the small victories.
With this structured approach, you’re not just wishing to sing better, you’re learning how to sing better, one practice session at a time.
FAQs
1) How Long Does It Take To Get Better At Singing?
Most singers notice a real improvement in control and tone within 4 to 6 weeks of consistent daily practice. Significant, more stable results often take 3 to 6 months of dedicated effort.
2) Can I Increase My Vocal Range?
Yes, almost every singer can increase their vocal range. Safe and consistent practice with exercises like pitch sirens and scales will gradually expand your access to higher and lower notes.
3) What’s the #1 Mistake Beginners Make?
The most common mistake is singing from the throat, which causes strain and a thin sound. Focus on powering your voice with deep breath support from your diaphragm to create a fuller, healthier tone.
4) What Should I Drink to Sing Better?
Water is the absolute best drink for your voice as it keeps your vocal folds hydrated. Aim for room-temperature water throughout the day and try to limit dehydrating drinks like alcohol and caffeine.



