Dubbing helps your videos and audio feel local while keeping emotion and timing intact. This guide shares seven practical strategies that make dubbing work feel professional, relatable, and ready for a global audience.
In order to improve your chances of succeeding in the market, you can leverage dubbing to reach more audiences. We’ll explain dubbing and talk about some of the helpful strategies you can use.
Key Takeaways
- Local voice casting makes characters feel authentic.
- Script adaptation wins over literal translation for timing and tone.
- Strong direction and careful lip sync preserve emotional impact.
- AI tools speed up drafts, human review preserves nuance.
- Use shared glossaries and QA to scale across markets.
- Budget, licensing, and platform rules all play a role in success.
Why Dubbing Helps Reach New Viewers
According to Business Research Insights, the global dubbing market is worth more than USD 2.2 billion today, showing that studios and brands see real value in localized audio.
It is no longer just about films; training content, promos, and even tutorials now rely on dubbing to connect with new audiences.
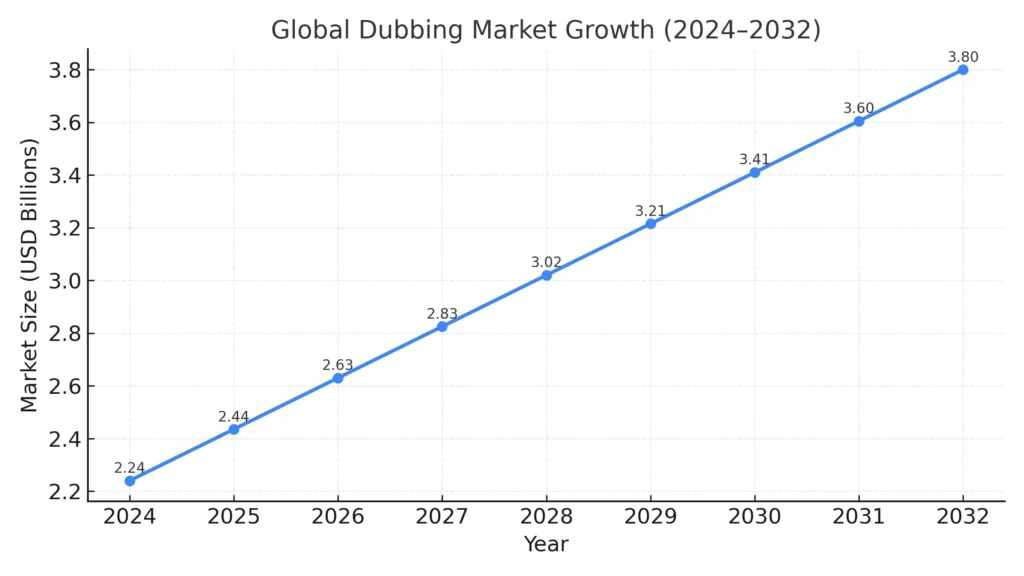
Source
Dubbing versus voice over, short answer
As explained by Slator, dubbing replaces the original spoken track and matches lips and expressions, while voice over overlays a translated voice on top of the original. For immersive stories, dubbing usually delivers the stronger experience.
Cast Local Voices That Match the Role
Casting is central to how audiences connect with content. Research into localization shows that viewers quickly judge whether a voice feels believable. Imagine a teenage character speaking with the tone of a middle-aged executive. The mismatch can pull people out of the story within seconds.
I once saw a campaign where the same actor voiced three lead roles. The audience feedback was immediate: “all the characters sound identical.” The brand ended up scrapping the audio and re-recording everything, wasting weeks of work.
Investing in strong local casting may seem costly at first, but it prevents expensive mistakes and builds trust with audiences. Creating that connection also depends on the recording space itself, since the acoustic workplace ambiance shapes how natural a voice will sound once localized.
Adapt Scripts to Fit Timing and Meaning
Literal translations almost never work for dubbing. Jokes, idioms, and cultural references often lose their punch when copied word for word. Skilled adaptors rewrite lines to fit the rhythm of the scene, so the dialogue flows naturally and still matches the lip movements.
Take humor as an example. A French pun might have no English equivalent, but a clever adaptor can reframe it with a locally relevant joke. This approach takes more time, but it is what makes the final product feel natural rather than forced.
Direct Performances to Match the Original Tone
Voice actors do not just need scripts; they need guidance. A reference clip, notes on tone, and live coaching during recording sessions keep the performance aligned with the original intent. Without direction, even experienced actors can drift into the wrong pacing or energy.
In one drama project, a serious argument scene was dubbed too flat, and the tension vanished. The fix was simple: stronger direction. Once the actor was asked to mirror the original emotion more closely, the entire scene came alive.
Tight Lip Sync Keeps Viewers Engaged
Mismatched lips and audio make any video look unprofessional. Editors often work frame by frame, adjusting timing and syllables until the words align with mouth movements, but the process starts earlier with clean recordings.
Choosing the right types of microphones ensures that every detail is captured clearly, making syncing smoother.
A training company I know skipped mobile testing before launch. On desktops, the sync looked fine. On phones, the lag was painfully obvious. They had to redo hours of footage. That small mistake cost weeks of time and budget.
Use AI to Scale, Humans to Preserve Nuance
Today, AI dubbing powered by tools like Synthesia offers a faster and more cost-effective way to produce multiple language versions. It can create draft audio in many languages in a fraction of the time. But here is the catch: AI often misses subtle emotion. Sarcasm sounds flat, humor feels off, and dramatic moments lose impact.
One company I worked with used an AI marketing tools for product explainers, and it worked fine. Straight narration does not need much emotional depth. But when they tried it on customer testimonial videos, the voices sounded robotic and insincere. The lesson is simple: AI is powerful for scale, but humans are still the ones who bring authenticity.
Industry guides such as Synthesia’s documentation show how this hybrid workflow helps companies scale while still protecting performance quality. Reliable equipment also makes a difference. The right audio accessories such as studio headphones and pop filters help capture clear recordings whether the voices come from AI or humans.
Quick Decision Table: AI or Human Dubbing
| Use Case | Recommended Approach | Why It Works |
| Short promos and product demos | AI first pass with light human edit | Fast turnaround with modest quality needs |
| Narrative series or major ads | Professional human actors with strong direction | Preserves emotional nuance and builds audience trust |
| High-volume market testing | AI drafts plus selective human polish | Speeds production while keeping key assets authentic |
Meet Accessibility and Delivery Standards
The W3C Web Accessibility Initiative highlights why captions and audio descriptions are essential for audiences with hearing or vision challenges. Adding them is not just a best practice; it is often a compliance requirement.
Skipping accessibility risks excluding entire groups of viewers and may even limit distribution on platforms that enforce accessibility standards.
Plan a Multi Market Workflow for Efficiency
Managing dubbing across multiple regions can become chaotic without a clear process. Shared glossaries, consistent style sheets, and QA checklists keep teams aligned and reduce duplicated work.
For example, Germany and Austria can often share the same adaptation with only small tweaks.
Studios that fail to coordinate often end up with inconsistent voices, mismatched terms, or wasted recording sessions. Planning the workflow upfront does not just save time, it makes the final content feel unified across markets.
Production Checklist You Can Copy
- Script adaptation sign off from a local reviewer.
- Cast sheet with voice notes and references.
- Recording session with director brief and alternate takes.
- Editing passes for lip sync and timing tweaks.
- Delivery package with localized audio, captions, and metadata.
- Review by native speakers before final release.
What Drives Dubbing Costs?
Budgets for dubbing vary widely, but a few main factors drive costs:
Voice talent fees: professional actors charge more than AI or non-native speakers, but their quality often pays off by making the content feel authentic.
Studio time and editing: longer projects with many takes or complex lip sync require more hours in production, which raises costs.
Script adaptation: hiring skilled adaptors adds upfront cost but prevents mistakes that lead to expensive re-recordings.
Market volume: dubbing into multiple languages at once is usually more efficient than doing them separately, since teams can reuse assets and streamline workflows.
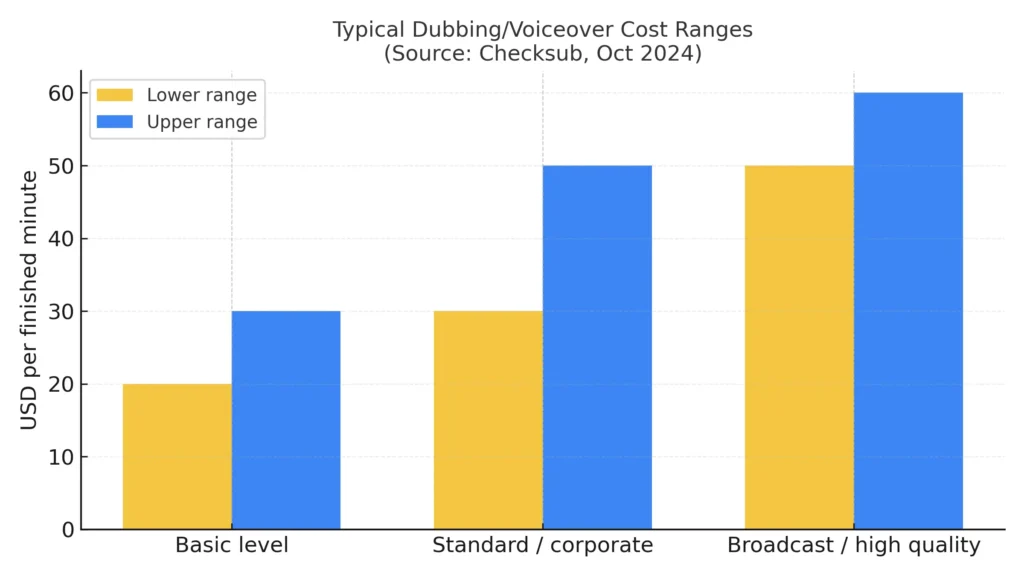
Protecting Voice Talent and Managing Rights
As reported by The Guardian, voice actors and unions have raised concerns about synthetic voice cloning. Contracts should now clearly cover consent, rights, and reuse terms.
Legal considerations go beyond voice cloning. Ownership of localized scripts, licensing of dubbed audio, and union rules can all impact distribution.
Platform and Distribution Requirements
Different platforms have different rules. Netflix requires specific file formats and audio quality levels for dubbed tracks. YouTube flags content without proper captions. Corporate LMS systems often demand transcripts alongside dubbed audio.
Measure What Matters
Dubbing is creative work, but it also needs measurement. Track watch time, completion rates, and skip rates before and after localized releases. Run small A B tests between subtitled and dubbed versions. These insights show which markets respond best and where to invest next.
Conclusion
Dubbing connects content to global audiences when done with care. Strong casting, smart adaptation, and quality equipment keep performances natural, while AI speeds up the workflow when paired with human review.
By budgeting carefully, meeting accessibility standards, managing rights, and tracking results, you can expand into new markets with confidence.
FAQs
1) Is Dubbing Always Better Than Subtitles?
Not always. Subtitles preserve the original voice, but dubbing makes content easier for audiences who prefer listening. Testing both is the best way to decide.
2) How Many Languages Should We Start With?
Start with your top markets. Release pilots, measure response, and then expand step by step.
3) How Long Does Dubbing Usually Take?
A short promo can be finished in days, while a full series episode with multiple characters may take weeks.
4) What Factors Affect Dubbing Costs?
Main drivers include voice talent fees, studio time, script adaptation, and the number of markets targeted.



